A 0.06mm2 14.7-to-20.2GHz Quad-Core VCO Enabled by the Folded Circular Transformer Achieving 201.1dBc/Hz FoMT and 203.4dBc/Hz FoMA
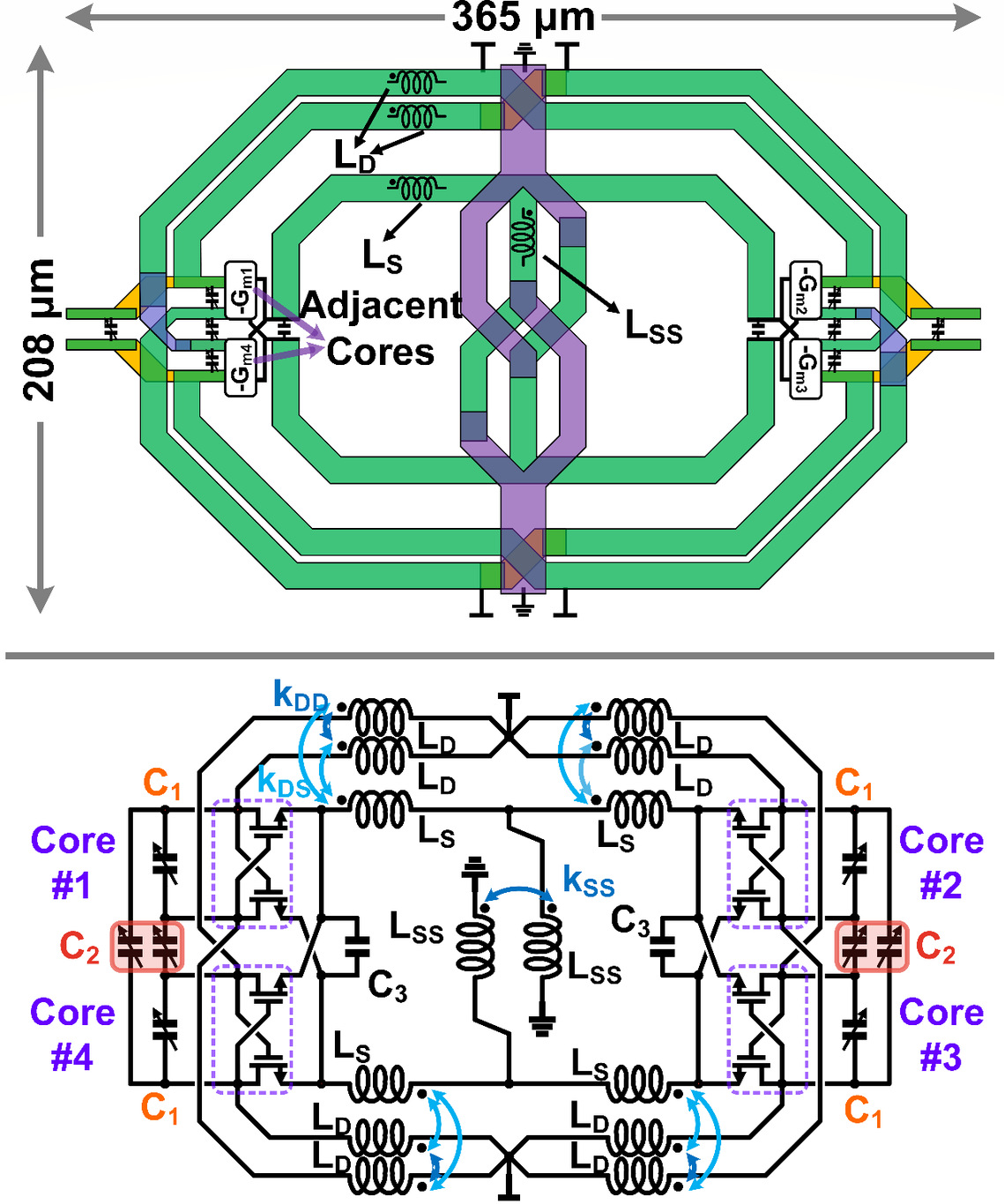
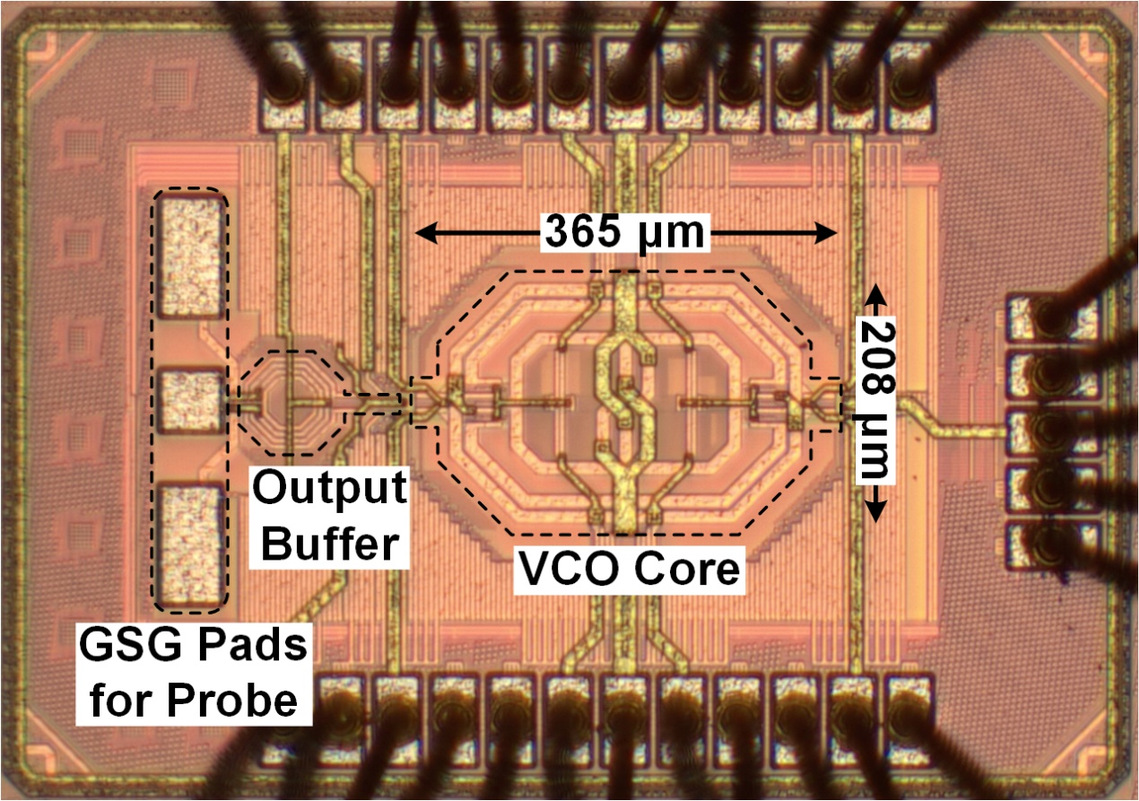
RFICAE team proposes a small-area, high-performance, strongly synchronized quad-core voltage-controlled oscillator (Quad-Core VCO) based on a folded circular transformer. Aiming at the difficulties of the traditional Quad-Core harmonic oscillator, such as large area, large phase noise penalty under frequency mismatch, and high parasitism in the synchronized network, a passive design of folded circular transformer is proposed. This design not only greatly compresses the on-chip area occupied by the four cores, but also exists multiple inductive synchronization paths and supports the introduction of inter-core capacitance as a capacitive synchronization path, thus forming a low-parasitic magnetic-electric field synchronized network, which greatly reduces the phase noise penalty caused by the frequency mismatch among cores. In addition, the current path of the passive supports quality factor enhancement in both differential and common modes and supports high-quality common-mode second-order harmonic shaping for 1/f3 noise suppression. The quad-core oscillator chip is implemented in 28nm CMOS process and covers a frequency range of 14.7 to 20.2GHz with a power consumption of 5mW and an area of 0.06mm², achieving FoMA and FoMT of 203.4 and 201.1dBc/Hz at 10MHz offset, respectively. Moreover, it shows a 1/f3 noise corner frequency of 350 to 700kHz.
The work was published as “A 0.06mm2 14.7-to-20.2GHz Quad-Core VCO Enabled by the Folded Circular Transformer Achieving 201.1dBc/Hz FoMT and 203.4dBc/Hz FoMA” in the leading international conference on integrated circuits, 2025 VLSI. FoMA” was published in the top international IC conference 2025 VLSI. Tincheng Ou, an undergraduate student at the School of Microelectronics, Fudan University, is the first author. The corresponding authors are Professors Na Yan and Hao Xu from Fudan University.